K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) – Theory
K-nearest neighbors (KNN) algorithm is a type of supervised ML algorithm which can be used for both classification as well as regression problems. However, it is mainly used for classification problems in the industry.
Following are the some important points regarding KNN-algorithm.
- K-Nearest Neighbor is one of the simplest Machine Learning algorithms based on Supervised Learning technique.
- K-NN algorithm assumes the similarity between the new case/data and available cases and put the new case into the category that is most similar to the available categories.
- K-NN algorithm stores all the available data and classifies a new data point based on the similarity. This means when new data appears then it can be easily classified into a well suite category by using K- NN algorithm.
- K-NN is a non-parametric algorithm, which means it does not make any assumption on underlying data.
- It is also called a lazy learner algorithm because it does not learn from the training set immediately instead it stores the dataset and at the time of classification, it performs an action on the dataset.
- KNN algorithm at the training phase just stores the dataset and when it gets new data, then it classifies that data into a category that is much similar to the new data.
Now let’s understand the algorithm with an example.
Suppose, we have an image of a creature that looks similar to cat and dog, but we want to know either it is a cat or dog. So for this identification, we can use the KNN algorithm, as it works on a similarity measure. Our KNN model will find the similar features of the new data set to the cats and dogs images and based on the most similar features it will put it in either cat or dog category.
Why do we need KNN algorithm?
Suppose there are two categories, i.e., Category A and Category B, and we have a new data point x1, so this data point will lie in which of these categories. To solve this type of problem, we need a K-NN algorithm. With the help of K-NN, we can easily identify the category or class of a particular dataset. Consider the below diagram:
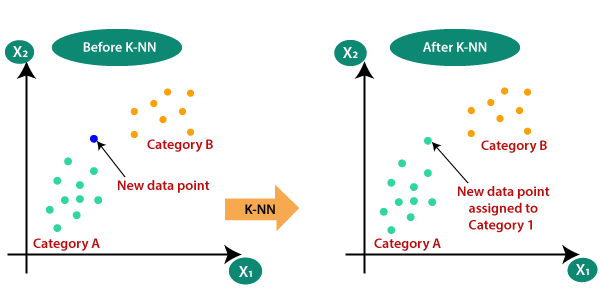
How does K-NN work?
To implement KNN algorithm you need to follow following steps.
- Step-1: Select the number K of the neighbors
- Step-2: Calculate the Euclidean distance of K number of neighbors
- Step-3: Take the K nearest neighbors as per the calculated Euclidean distance.
- Step-4: Among these k neighbors, count the number of the data points in each category.
- Step-5: Assign the new data points to that category for which the number of the neighbor is maximum.
- Step-6: Our model is ready.
Suppose we have a new data point and we need to put it in the required category. Consider the below image:
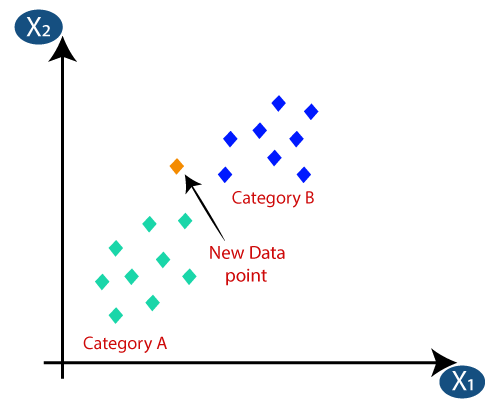
- First of all, we will choose the number of neighbors, so we will choose the k=5.
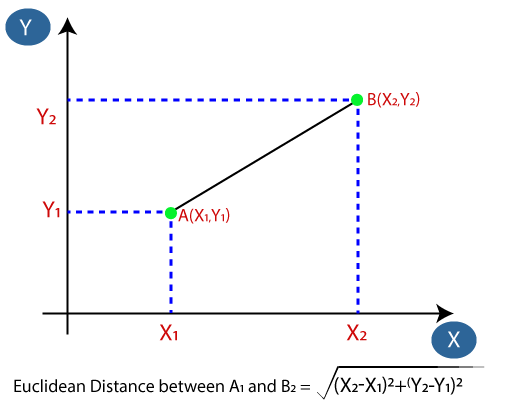
- Next, we will calculate the Euclidean distance between the data points. The Euclidean distance is the distance between two points, which we have already studied in geometry. It can be calculated as:
By calculating the Euclidean distance we got the nearest neighbors, as three nearest neighbors in category A and two nearest neighbors in category B. Consider the below image:
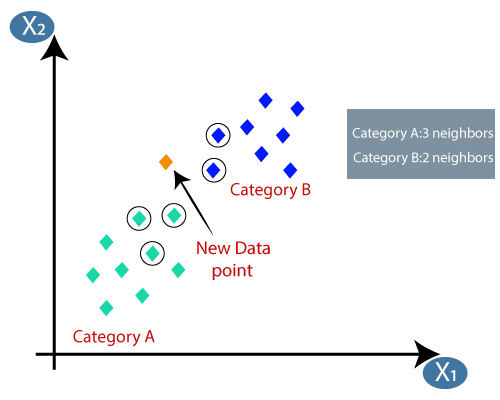
- As we can see the 3 nearest neighbors are from category A, hence this new data point must belong to category A.
How to select the value of K in the K-NN Algorithm?
Below are some points to remember while selecting the value of K in the K-NN algorithm:
- There is no particular way to determine the best value for “K”, so we need to try some values to find the best out of them. The most preferred value for K is 5.
- A very low value for K such as K=1 or K=2, can be noisy and lead to the effects of outliers in the model.
- Large values for K are good, but it may find some difficulties.
Pros and Cons of KNN:
Pros-
- Very Simple
- Training is trivial
- Works with any number of classes
- Easy to add more data
- It has few parameter such as K and distance matric.
Cons-
- The computation cost is high because of calculating the distance between the data points for all the training samples.
- Categorical features don’t work well
- Not good with the high dimensional data
Leave a Reply